Mobile Security – From CIA to the enemy from within!
November 15, 2017
A report written by Tomás Moral for the Mobile Business Class 2017 held by Mr. Corsin Decurtins:
A packed four hours course with lots of information about Mobile Security. Mr. Decurtins did not lie when he promised that after this course we will be more paranoid about our digital security. He also was right that 4 hours are not enough to go deep into the topic.
Organizations, Businesses as well as all others depend on IT systems and technology. This enables a lot and brings a lot of features, but also threats and attacks.
IT Security usually does not just fail a little bit, it fails catastrophically and completely, affecting thousands or millions of users. Hacking IT systems is a multi-billion dollar industry World-wide. Behind of the attacks are highly organized and networked Organizations with private stakeholders and sometimes even government structures.
IT becomes more and more mobile. We started out with computers and IT systems that took up whole floors or even buildings. Today we have computers that are much smaller and more powerful – in your pocket, watch, wrist, bicycle, cars, buildings, fridge and even in your flower pots. Everything is connected, it is Smart, automated, ubiquitous – this makes our systems vulnerable for attacks, remote attacks and automated attacks.
We perceive mobile computing much less as IT than conventional “computers” – Therefore we also treat security concerns differently. Mobile device include sensors, capable of collecting very personal data. Data Centers are protected by physical and virtual security systems. These are high-security installations, monitored and protected by dedicated teams of security experts. Mobile devices do not enjoy the same level of protection
The risk of loss and theft is increased by using mobile devices. Also others can look over your shoulder and spy on you doings. We are constantly leaving identifying traces in the IT environment, because we are always looking for new wireless networks without checking their security behind.
Not all systems require the same level of protection and security. But the number of devices and apps is growing. The capabilities of the apps are increasing and the complexity and sensitivity of the data and Systems is higher then ever.
Summarized we can say: We have more assets that are more valuable and more exposed this means: more attackers with more ways to exploit security vulnerabilities
It is not just about you, your business or representatives of a business. There is a lot of sensitive data and valuable services that should be protected and also the access to that information. Often there is sensitive data from customers. They trust you to keep their data safe and secure. If you have security breaches, they are also affected.
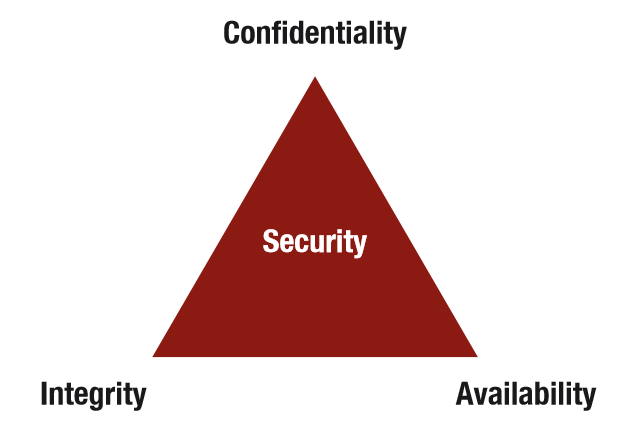
The CIA Triad
Information and services are only available to authorized people and systems
Data is consistent (no logical conflicts) – Data has not been manipulated or forged – Data can only be changed by authorized people and systems
Availability
Data and services are available for people and systems when required
Theoretical security is an absolute thing. Either you have full confidentiality, integrity and availability or you do not. In practice, security is much more relative. Absolute security is normally not possible or at least not practical, reasonable or affordable. Security is very difficult to assess. Not having any security issues, does not mean that you are secure. Knowing for sure that you have all three properties is not possible. Security and measures to ensure security, are often in conflict with price, usability, user experience or practicality.
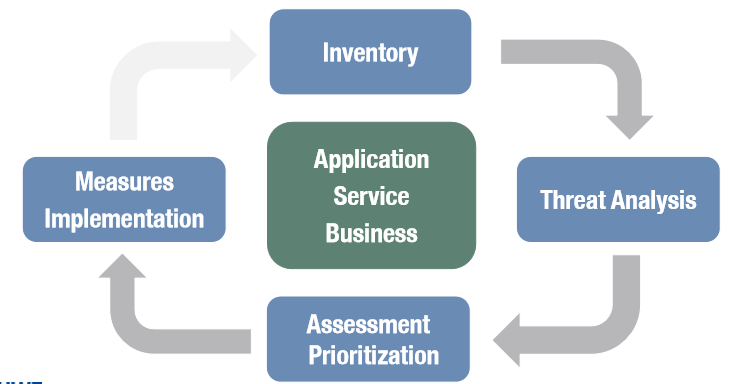
Security Engineering Process
What are we trying to protect?
Data, Privacy, identity, anonymity and Meta-Data Functionality. What, if we fail to protect the assets? Direct damage, losing money, losing competitive advantage, Embarrassment, reputational damage and losing trust.
Stealing data, money, privileges, Espionage, Blackmail, Identity Theft, Destroying reputation, fun Activism, War or Hacking systems in order to use them to attack other systems
Technical Vulnerabilities, known exploits Operational and Process Vulnerabilities. Attacks making use of operational and process weaknesses and Social Engineering by attaking unsuspecting people
Criminal organisations, Competitors, Governments, Activists and Researchers. Important there can be Attacks from the outside and from within an organization.
There are other threats such as, natural disasters, Flooding, Fire, Technical failures, Software bugs, Disk crashes, Network outages, Power failures or Human error.
It is important to make a proper Risk Analysis and assess the possible threats. As soon as the analysis is done, prioritize based on – Attack probability, damage, effort and Counter measures.
Define Measures and Implement Security infrastructure, protocols and very important, use security tools such as encryption, firewalls and malware scanners.
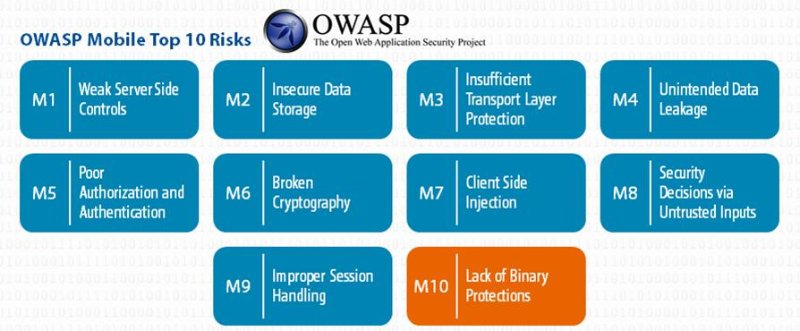
OWASP Mobile Top 10 Risks
The security features of PIN codes and passwords rely on the fact that they are impossible or at least very difficult to guess. In order to be difficult to guess, they have to be random.
Computers are getting faster and faster. They are able to try out more and more passwords in shorter amounts of time. That essentially means that passwords are getting easier and easier to guess. Simple solution: Use longer passwords. Problem: The speed of computers is growing all the time, the capacity for humans to remember passwords is not. And entering long passwords on mobile devices is very tedious and error-prone. And even more problematic is that we often are entering passwords on mobile devices in public.
These are different things. Authentication is the process of proving something. In IT-language proving usually means that you have an access right. Authentication does not directly say anything about the person or system that has a right. A traditional example of an authentication is a key.
Identification is the process of proving that you have a particular identity. People and machines can have multiple identities. Think of pseudonyms. An old school example of an identification is a membership card or a credit card. An identification does not directly include an authentication.
The processes of authentication and identification can often be combined. Some means of authentication are also means of identification. For example a passport proofs that you are a particular person (identity), but also that you are a citizen of a particular country and thus have some associated rights.
Two, independent mechanisms for authentication or identification Ideally from two different categories like for ex. things, information or bio-metrics.
Examples: Bank card and PIN code or key (for the door) and password to disarm the alarm system.
Encryption Encoding of data in such a way that only authorized parties can access it. Based on mathematical operations and algorithms. Encryption algorithms are normally standardized and Encryption keys provide the secret element
There are two known Encryption Systems. Symmetric Encryption: the same key is used to encrypt and decrypt data, and Asymmetric Encryption: key pairs with different, but related keys are used to encrypt and decrypt data
Security is not just an important topic during design and implementation. Security is also very important during operations. This is when the actual attacks happen, even if the attacks were made possible during design and implementation. Security Monitoring is a very important aspect. This is much trickier on mobile devices than on servers in high-security data centers.
Mobile Platforms Security is an important topic for providers of Mobile Platforms. If your mobile app is hacked, it also reflects badly on the platform provider. Security is a selling point that attracts users, developers and Businesses. Mobile platforms have sophisticated security features.
If you think that security is all about coding, cryptography, mathematics, you could not be more wrong. The human element is very important in IT security. If you think about security, you have to include people in the mix. Humans are fallible and lazy. Humans are mostly optimistic and have limited capabilities. Sometimes they do the wrong things, because they do not know any better and worse than that, they do the wrong things, even though they know exactly that they are doing the wrong things.
If you want to attack a system, start with the weakest part of the system. Humans are often the weakest parts. Social Engineering focusses on hacking humans. The tools and protocols might be a bit different, but the rest is the same as hacking IT systems. Humans have weaknesses and vulnerabilities. Social Engineering focus on exploiting them. Defending against social engineering is very, very hard.
Security is always a quality that is hard to grasp. Nobody can tell you how much exactly you have to invest. Security aspects are often in conflict with other topics such as Costs, Time to Market, User Experience / Usability, Complexity and did I mention Costs.
Security is expensive. Nobody can tell you how much you have to spend on it exactly. If you do it right, you will never encounter a situation that would justify investing in security. No security is probably even more expensive!
Security is not a binary thing. Security is a continuous topic, so you are never done with security. You never know when you have done enough. You only ever find out when you have not done enough! You have to know what you are trying to protect. You have to guess who and what you are trying to protect yourself from.
Security can be expensive, no Security can be even more expensive. Get help from specialists, but do not delegate everything to the specialists. Ultimately, you are responsible and only you can make some decisions
Not having data means that nobody can steal it, not having a functionality means that nobody can exploit it. Do not rely on one single measure to protect you. Things should be protected by multiple, independent layers of security measures. And do not forget the enemy from within!
Unser Newsletter liefert dir brandaktuelle News, Insights aus unseren Studiengängen, inspirierende Tech- & Business-Events und spannende Job- und Projektausschreibungen, die die digitale Welt bewegen.