Digital Risk – Opportunities to shine
Oktober 23, 2017
Aus dem Unterricht des CAS Digital Masterclass mit Ralph Hutter berichtet Samantha Mueller:
What risk are there in the digital world? Answering this question and highlighting the many issues and challenges facing cyberspce was the objective of this class lead by Ralph Hutter the HWZ CAS Digital Risk Management Course Administrator.
It is impossible to keep up with all the screen shots that could be included to illustrate all the digital risks in the internet today. The following are just three examples of what can happen when criminal minds or rogue states decide to use the internet for their own gain: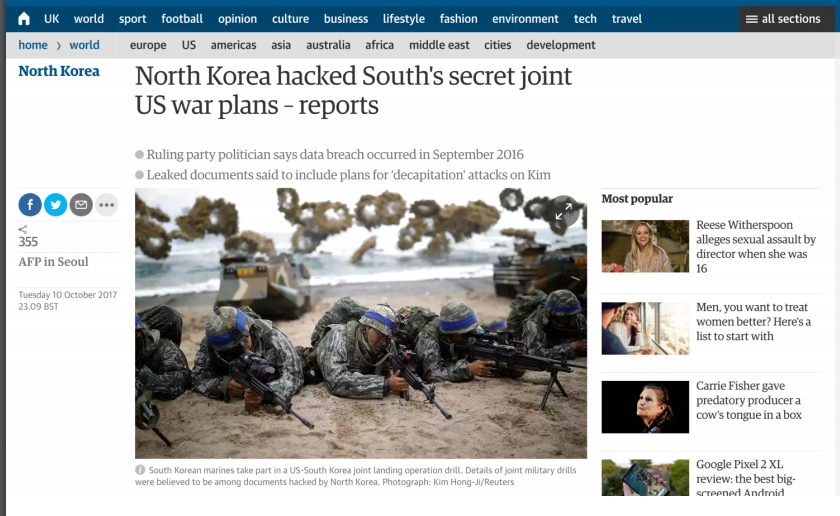
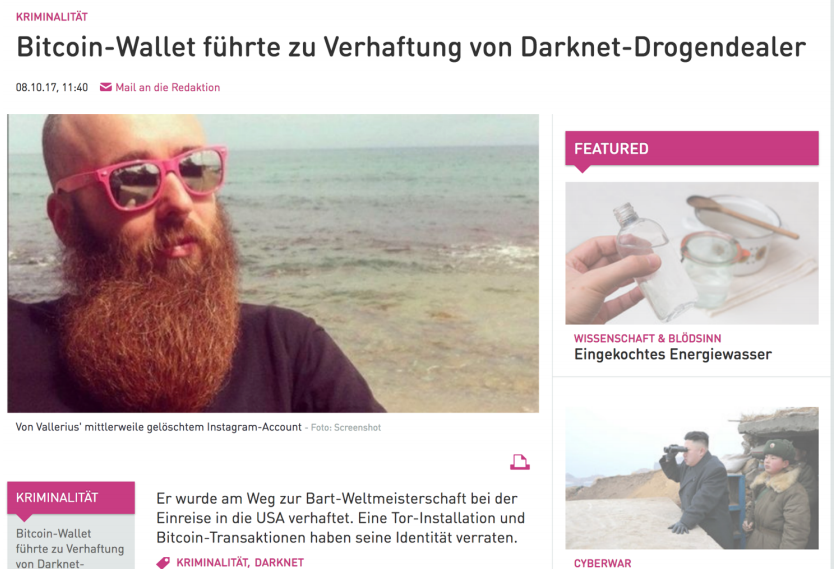
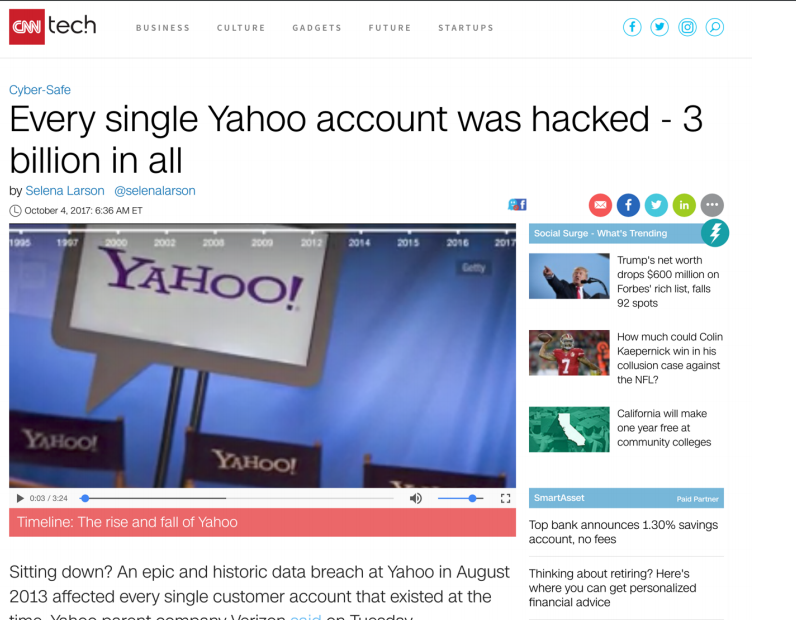
The world is a dangerous place, Elliott, not because of those who do evil, but because of those who look on and do nothing.
– Mr. Robot
Digital technologies raising new legal questions and causing reputation damage
All the data that is being collected via all our digital devices opens up new dimensions of legal regulation. For example, can data Alexa (Amazon’s intelligent personal assistant) might have recorded be used in a murder case? This is an actual case currently making headlines in the US State of Arkansas.
Another case closer to home, is the malfunctioning of the Postfinance E-Banking systems. The reason is still unknown, but this has caused huge reputation damage to the company. Several more cases were highlighted showing how there are many new risks in the evolving digital world today.
Cyber Crime Statistics
KOBIK (Koordinationsstelle zur Bekämpfung der Internetkriminalität) The Swiss agency for fighting cyber crime) released some frightening numbers in its Annual Report 2014. The number of registered complaints about cybercrime have dramatically increased in particular with regards to financial crime. Fraud, phishing, data destruction, sextortion, stolen email accounts, romance scam, etc. It is a big business!
The Enisa threat landscape report 2016 (European Commission) indicates that the picture is the same in Europe as in Switzerland. The number one issue is malware, second place are web based attacks on the web browser technology and third place are web application attacks (native apps).
An additional report, Emerging Cyber Threats Report 2016, highlighted 4 key themes:
Who are these Cyber attackers?
Hacktivists such as Anonymous who don’t do harm could be seen as serving a positive purpose in cyber space in that they bring “justice” to unfair operators. Not all hackers have malicious intent but can be a big nuisance. However, fake news produced by troll farms are usually sponsored by a state and have an objective of harming or influencing a process or institution. For example the Russian involvement in the US elections.
Case Studies
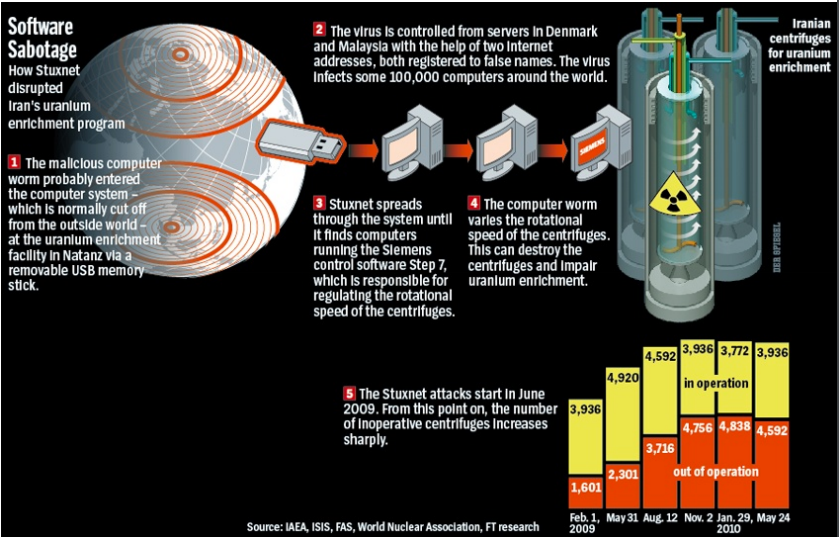
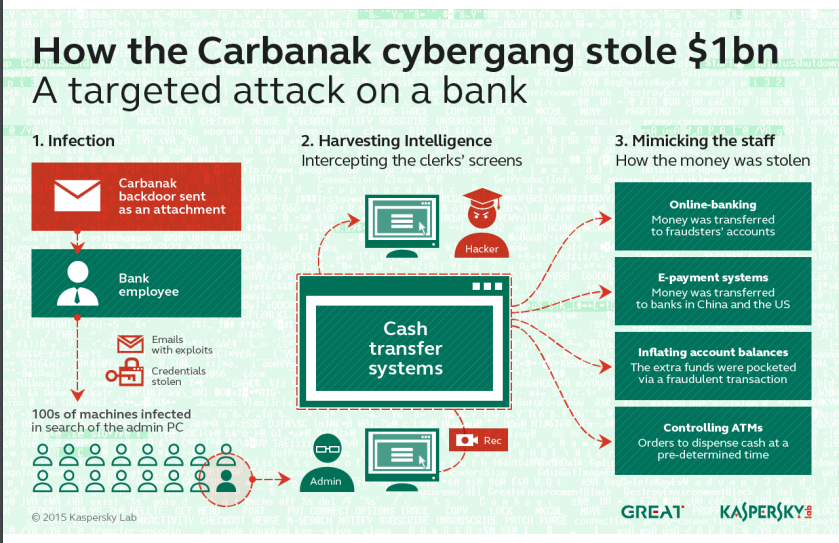
What is the role of the authorities in Switzerland?
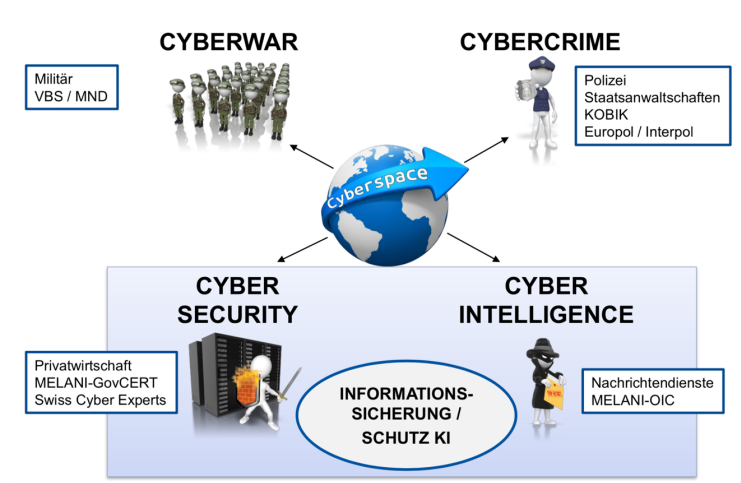
There are two organizations in Switzerland for cyber security: MELANI (oversight of infrastructures of national security and prevention of attacks) and KOBIK (The Cybercrime Coordination Unit). The two organizations have slightly different mandates which are detailed below: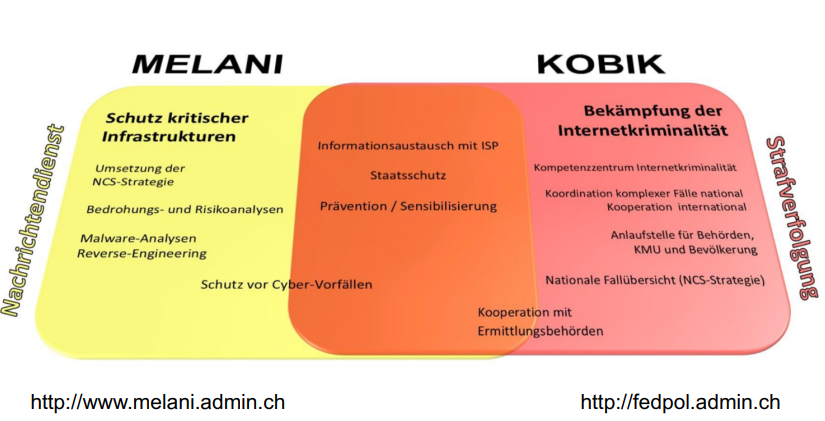
Group Work: Anatomy of a hack – Ransomware Attack
We watched a movie about how cyber criminals managed to hijack a company’s IT with randsomware in exchange for bitcoins. We then reviewed how they did it. Here is how they did it:
Step 1: Social Engineering: Researching about the target person and mimicking their behaviour to send an email to staff with an malware attachment.
Step 2: Employee opens email and malware is installed blocking the system
Step3: Send ransom demanding bitcoins for a unlock code
Results: Company stock drops, company has huge reputational damage due to data leak and CEO resigns.
What was the motivation of this attack? The bitcoins from ransom plus profiting from the drop in the stock.
How to best preventing attacks on personal data
The number of attacks have increased exponentially since 2004. To check your personal account got to: https://haveibeenpwned.com/ and enter your email to see where your data has been illegally accessed. It is scary!
To protect your accounts, it is recommended that you change your passwords and don’t reuse the password for other accounts. Manage these passwords in an online safe for example on:
The best passwords have more than 8 letter with upper and lower cases including numbers and no words or phrases.
Secure Browsing
According to the Kaspersky Report, 48 percent of attacks come via browser! Stay away from apps and sites that offer free services which would normally be expensive. Example, a free photoshop app. If it seems to good to be true it will most likely infect your system.
Here some more tips on how to best surf and ensure you protect your system from attack:
Possible solutions for backing-up your data
Key Learnings from the course
Unser Newsletter liefert dir brandaktuelle News, Insights aus unseren Studiengängen, inspirierende Tech- & Business-Events und spannende Job- und Projektausschreibungen, die die digitale Welt bewegen.